Embracing New Literacies and 21st Century Skills

Top 3 Strong 21st Century Literacies
Science Literacy
Justifications/Reasons:
- Undergraduate program training
- Natural curiosity about the world and how things work
- Strong analytical and problem-solving skills
- Ability to think critically and evaluate information objectively
- Proficiency in interpreting data and drawing conclusions
- Eagerness to explore scientific concepts through experiments
Arts and Creativity Literacy
Justifications/Reasons:
- Expressive and imaginative thinking
- Ability to communicate ideas through various artistic mediums
- Strong sense of aesthetics and design
- Open-mindedness and willingness to experiment with new techniques
- Capacity to think outside the box and generate innovative solutions
Cyber/Digital Literacy
Justifications/Reasons:
- Proficiency in using technology and digital tools effectively
- Strong understanding of online safety and security measures
- Ability to navigate digital platforms and information systems efficiently
- Skill in digital communication and collaboration
- Adaptability to new technologies and willingness to learn and explore digital innovations
Top 3 Weak 21st Century Literacies
Financial Literacy
Justifications/Reasons:
- Lack of exposure to financial concepts and practices
- Limited access to resources or education on financial management
- Cultural taboos surrounding money discussions within the family or community
Social Literacy
Justifications/Reasons:
- Limited social interactions due to shyness or social anxiety
- Cultural differences in social norms and expectations
Multicultural and Global Literacy
Justifications/Reasons:
- Limited exposure to diverse cultures and perspectives
- Lack of access to multicultural education or resources
- Ethnocentrism and biases that hinder understanding and appreciation of different cultures
- Raised by traditional family customs
Reflection
In today's fast-paced and ever-changing world, having a diverse set of 21st-century literacies and skills is crucial for success. By identifying my strengths and weaknesses in these areas, I can focus on improving my weaker skills while leveraging my strengths to excel in my personal and professional endeavors. This self-awareness allows me to adapt to various challenges, communicate effectively, think critically, and collaborate with others across different fields, ultimately making me a more versatile and valuable individual in the modern workforce. I believe that being a generalist in terms of literacy skills is better than being strong in a singular area.
In terms of financial literacy, I aim to enhance my understanding of topics such as accountancy, business, and management, especially since these areas were not covered in my high school curriculum. As someone in the STEM field, I acknowledge the importance of financial skills in my future career and personal finances, including aspects like retirement planning and investment strategies.
Regarding social literacy, I recognize that I sometimes struggle with anxiety in communication situations. To address this, I actively seek opportunities to improve my communication skills, such as participating in public speaking engagements or volunteering for tasks that require effective verbal and written communication.
In terms of public engagement, I have discovered that I excel in digital communication and technology literacy, which has been beneficial in streamlining processes and fostering collaboration within my team. However, I have identified a weakness in data presentation and interpretation. To address this gap, I have enrolled in online courses to enhance my skills in conveying complex data in a clear and understandable manner for a broader audience.
By actively assessing and addressing both my strengths and weaknesses, I have not only advanced professionally but also gained confidence in approaching new challenges with a proactive mindset.
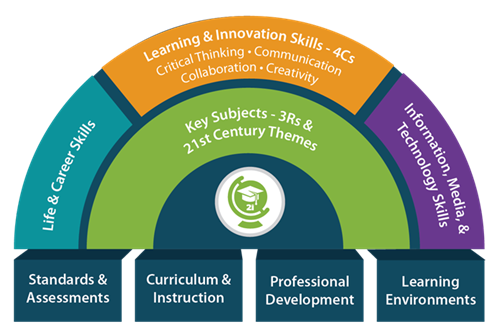
21st Century Literacies: Problems, School Subjects, and Teaching Strategies
1. Global and Multicultural Literacy
Current World/National/Local Problems and Issues:
- Cultural misunderstandings and conflicts
- Xenophobia and racism
- Lack of cultural awareness and sensitivity
- Global migration and refugee crises
Most Suitable School Subjects or Topics:
- Social Studies
- Geography
- History
- Language Arts
- World Languages
Suggested Teaching and Learning Strategies:
- Students research different cultures and present their findings.
- Virtual or physical exchange programs to interact with students from different cultures.
- Scenarios that require students to navigate cultural misunderstandings.
- Reading and discussing books from diverse authors and perspectives.
2. Media Literacy
Current World/National/Local Problems and Issues:
- Spread of misinformation and fake news
- Bias in media representation
- Influence of media on public opinion and behavior
- Lack of critical thinking skills when consuming media
Most Suitable School Subjects or Topics:
- English/Language Arts
- Social Studies
- Technology and Computer Science
- Civics
Suggested Teaching and Learning Strategies:
- Analyzing news articles and media content for bias and credibility.
- Creating their own news stories or documentaries.
- Debating current events and the role of media.
- Journalists and media professionals discussing their work.
3. Cyber/Digital Literacy
Current World/National/Local Problems and Issues:
- Cyberbullying and online harassment
- Data privacy and security concerns
- Digital divide and unequal access to technology
- Misuse of digital tools and platforms
Most Suitable School Subjects or Topics:
- Computer Science
- Information Technology
- Social Studies
- Health Education
Suggested Teaching and Learning Strategies:
- Teaching responsible and ethical use of technology.
- Hands-on activities to understand online security.
- Using digital tools for group work and presentations.
- Using online resources for at-home learning and classroom discussion.
4. Social Literacy
Current World/National/Local Problems and Issues:
- Social isolation and lack of communication skills
- Bullying and peer pressure
- Inability to work effectively in teams
- Low empathy and emotional intelligence
Most Suitable School Subjects or Topics:
- Social Studies
- Psychology
- Health Education
- Language Arts
Suggested Teaching and Learning Strategies:
- Emphasizing teamwork and collaboration.
- Practicing social scenarios and conflict resolution.
- Engaging in community service projects.
- Promoting emotional intelligence and empathy.
5. Financial Literacy
Current World/National/Local Problems and Issues:
- High levels of debt and poor money management
- Lack of savings and retirement planning
- Economic inequality and lack of financial knowledge
- Predatory lending and financial scams
Most Suitable School Subjects or Topics:
- Mathematics
- Economics
- Business Studies
- Social Studies
Suggested Teaching and Learning Strategies:
- Creating and managing a budget.
- Learning about investments and market dynamics.
- Financial advisors and bankers discussing money management.
- Real-world financial planning projects.
6. Ecological Literacy
Current World/National/Local Problems and Issues:
- Climate change and environmental degradation
- Pollution and waste management issues
- Loss of biodiversity and habitat destruction
- Sustainable development challenges
Most Suitable School Subjects or Topics:
- Science (Biology, Chemistry, Earth Science)
- Geography
- Environmental Studies
- Social Studies
Suggested Teaching and Learning Strategies:
- Visiting natural sites and learning about ecosystems.
- Environmental projects and sustainability initiatives.
- Hands-on activities like recycling programs and gardening.
- Investigating local environmental issues and proposing solutions.
7. Arts and Creativity Literacy
Current World/National/Local Problems and Issues:
- Decreased funding for arts education
- Limited access to arts and cultural experiences
- Lack of creativity in problem-solving and innovation
- Overemphasis on standardized testing
Most Suitable School Subjects or Topics:
- Visual Arts
- Music
- Drama/Theatre
- Language Arts
Suggested Teaching and Learning Strategies:
- Combining arts with other subjects like history or science.
- Encouraging imaginative expression.
- Showcasing student work to the community.
- Group art installations or performances.
8. Science Literacy
Current World/National/Local Problems and Issues:
- Misinformation about scientific topics (e.g., vaccines, climate change)
- Lack of interest and engagement in STEM fields
- Inequitable access to quality science education
- Gender and racial disparities in STEM careers
Most Suitable School Subjects or Topics:
- Science (Biology, Chemistry, Physics)
- Mathematics
- Technology
- Engineering
Suggested Teaching and Learning Strategies:
- Encouraging students to ask questions and conduct experiments.
- Integrating science, technology, engineering, and math in projects.
- Scientists and engineers discussing their work and research.
- Visits to science museums, research centers, and industry sites.
Reflection
In today's digital age, students are constantly bombarded with information from various sources, making the ability to discern credible information from misinformation a critical skill. Misinformation, often spread through social media platforms like Facebook and TikTok, can skew students' perceptions of reality and hinder their ability to think critically. For instance, during the COVID-19 pandemic, the Philippines saw a surge in misinformation about the virus and vaccines, complicating public health efforts and demonstrating the dire need for robust critical thinking skills to evaluate the veracity of online content.
Students frequently use digital tools and platforms, which raises concerns about the security of their personal information. Educators must navigate these issues to ensure that collaborative learning environments are safe and secure. The algorithms employed by social media platforms like Facebook can inadvertently expose users to privacy risks by harvesting data for targeted advertising. In the Philippines, where internet usage is high and social media plays a significant role in daily communication, educators must teach students how to collaborate online without compromising their personal information.
Economic problems also significantly impact the development of 21st-century skills. In many regions, here in our country, economic disparities can limit access to essential digital resources and technology, widening the digital divide. This divide hinders students' ability to develop literacy skills, as those without adequate access to technology are at a disadvantage. Addressing economic inequalities and ensuring equitable access to technology are vital steps in cultivating a digitally literate and skilled student population capable of thriving in a 21st-century learning environment.
Some challenges include integrating digital literacy, media literacy, and information literacy without compromising the depth of traditional subjects. It requires extensive planning to ensure these literacies complement rather than overshadow traditional learning goals. Resource availability and inequity is also an issue as we must ensure that all students have equal access to technology and resources. Students in economically disadvantaged areas may lack access to high-speed internet or modern devices, making it difficult to implement tech-heavy lessons. Solutions like offline resources or school-provided devices are not always feasible.
In both virtual and physical classrooms, students can easily become distracted by social media, games, or other online content. Implementing strategies like scheduled tech breaks and interactive activities can help maintain focus but requires constant adaptation. In terms of assessments, traditional testing methods may not effectively measure skills like digital collaboration or media analysis. Creating authentic assessments, such as project-based tasks or digital portfolios, can be more appropriate but requires significant effort to design and grade.
The access to information and artificial intelligence like ChatGPT online increases the risk of plagiarism. Tools like plagiarism detection software help but fostering a culture of academic integrity through education on proper citation and the value of original work is equally important. Another challenge is in helping students navigate and manage their digital identities responsibly. Students often lack awareness about digital footprints and the long-term implications of their online behavior. Integrating lessons on digital citizenship and online safety is crucial but requires sensitive and age-appropriate approaches. The pressure to maintain a social media presence and cyberbullying are also issues. Teachers need to be vigilant and proactive in identifying signs of mental health struggles, fostering an open environment for discussion, and providing resources to support services. Lastly, there must be open communication between 21st-century parents, students, and teachers to support student learning and well-being.

Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Integration into Education
1. No Poverty
Current Problems/Issues/Challenges:
- High rates of unemployment
- Lack of access to basic services
- Economic inequality
Suitable School Subjects/Topics:
- Economics
- Social Studies
- Mathematics
Suitable 21st Century Literacy/Skills:
- Financial Literacy
- Social Literacy
- Global and Multicultural Literacy
2. Zero Hunger
Current Problems/Issues/Challenges:
- Food insecurity and malnutrition
- Agricultural inefficiency
- Food waste
Suitable School Subjects/Topics:
- Biology
- Geography
- Home Economics
Suitable 21st Century Literacy/Skills:
- Ecological Literacy
- Science Literacy
- Global and Multicultural Literacy
3. Good Health and Well-being
Current Problems/Issues/Challenges:
- Access to healthcare
- Mental health issues
- Lifestyle diseases
Suitable School Subjects/Topics:
- Health Education
- Physical Education
- Biology
Suitable 21st Century Literacy/Skills:
- Science Literacy
- Social Literacy
- Digital Literacy
4. Quality Education
Current Problems/Issues/Challenges:
- Educational inequality
- Access to quality resources
- Teacher training and support
Suitable School Subjects/Topics:
- Education Theory
- Social Studies
- Technology
Suitable 21st Century Literacy/Skills:
- Digital Literacy
- Social Literacy
- Global and Multicultural Literacy
5. Gender Equality
Current Problems/Issues/Challenges:
- Gender-based violence
- Disparity in education and employment opportunities
- Cultural stereotypes
Suitable School Subjects/Topics:
- Social Studies
- Health Education
- Language Arts
Suitable 21st Century Literacy/Skills:
- Social Literacy
- Media Literacy
- Global and Multicultural Literacy
6. Clean Water and Sanitation
Current Problems/Issues/Challenges:
- Water pollution
- Lack of access to clean water
- Poor sanitation facilities
Suitable School Subjects/Topics:
- Science (Chemistry, Biology)
- Geography
- Environmental Studies
Suitable 21st Century Literacy/Skills:
- Ecological Literacy
- Science Literacy
- Social Literacy
7. Affordable and Clean Energy
Current Problems/Issues/Challenges:
- Reliance on fossil fuels
- Energy poverty
- Environmental impact of energy production
Suitable School Subjects/Topics:
- Physics
- Environmental Science
- Economics
Suitable 21st Century Literacy/Skills:
- Science Literacy
- Ecological Literacy
- Financial Literacy
8. Decent Work and Economic Growth
Current Problems/Issues/Challenges:
- High unemployment rates
- Job quality and security
- Economic disparities
Suitable School Subjects/Topics:
- Economics
- Business Studies
- Social Studies
Suitable 21st Century Literacy/Skills:
- Financial Literacy
- Social Literacy
- Global and Multicultural Literacy
9. Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure
Current Problems/Issues/Challenges:
- Outdated infrastructure
- Lack of innovation
- Industrial pollution
Suitable School Subjects/Topics:
- Engineering
- Technology
- Economics
Suitable 21st Century Literacy/Skills:
- Digital Literacy
- Science Literacy
- Financial Literacy
10. Reduced Inequalities
Current Problems/Issues/Challenges:
- Economic inequality
- Social and cultural discrimination
- Unequal access to opportunities
Suitable School Subjects/Topics:
- Social Studies
- Economics
- Civics
Suitable 21st Century Literacy/Skills:
- Social Literacy
- Global and Multicultural Literacy
- Media Literacy
11. Sustainable Cities and Communities
Current Problems/Issues/Challenges:
- Urban sprawl
- Pollution and waste management
- Affordable housing
Suitable School Subjects/Topics:
- Geography
- Environmental Science
- Urban Studies
Suitable 21st Century Literacy/Skills:
- Ecological Literacy
- Science Literacy
- Social Literacy
12. Responsible Consumption and Production
Current Problems/Issues/Challenges:
- Overconsumption
- Waste management
- Sustainable resource use
Suitable School Subjects/Topics:
- Economics
- Environmental Science
- Business Studies
Suitable 21st Century Literacy/Skills:
- Ecological Literacy
- Financial Literacy
- Science Literacy
13. Climate Action
Current Problems/Issues/Challenges:
- Climate change and global warming
- Extreme weather events
- Carbon emissions
Suitable School Subjects/Topics:
- Environmental Science
- Geography
- Physics
Suitable 21st Century Literacy/Skills:
- Ecological Literacy
- Science Literacy
- Social Literacy
14. Life Below Water
Current Problems/Issues/Challenges:
- Marine pollution
- Overfishing
- Coral reef destruction
Suitable School Subjects/Topics:
- Biology
- Environmental Science
- Geography
Suitable 21st Century Literacy/Skills:
- Ecological Literacy
- Science Literacy
- Social Literacy
15. Life on Land
Current Problems/Issues/Challenges:
- Deforestation
- Habitat loss
- Biodiversity decline
Suitable School Subjects/Topics:
- Biology
- Geography
- Environmental Science
Suitable 21st Century Literacy/Skills:
- Ecological Literacy
- Science Literacy
- Social Literacy
16. Peace, Justice and Strong Institutions
Current Problems/Issues/Challenges:
- Corruption and governance issues
- Human rights abuses
- Access to justice
Suitable School Subjects/Topics:
- Civics
- Social Studies
- Law
Suitable 21st Century Literacy/Skills:
- Social Literacy
- Media Literacy
- Global and Multicultural Literacy
17. Partnerships for the Goals
Current Problems/Issues/Challenges:
- Lack of collaboration between sectors
- Insufficient funding for SDG initiatives
- Policy and regulatory challenges
Suitable School Subjects/Topics:
- Social Studies
- Business Studies
- Economics
Suitable 21st Century Literacy/Skills:
- Social Literacy
- Financial Literacy
- Global and Multicultural Literacy
Reflection
Integrating Education for Sustainable Development (ESD) and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) into school subjects and curriculum is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it promotes global citizenship by helping students understand their role in addressing global challenges like climate change and poverty. It also encourages interdisciplinary learning, fostering connections across subjects and highlighting the complexity of sustainable development issues. Additionally, ESD cultivates critical thinking skills, empowering students to analyze real-world problems and develop innovative solutions.
In the context of the Philippines, integrating ESD and SDGs into the curriculum is vital for addressing local challenges and promoting sustainable development. For example, incorporating SDG 4 can emphasize the importance of inclusive and quality education for all, including marginalized communities in remote areas. Teaching about clean water and sanitation (SDG 6) aligns with efforts to improve water access in rural Philippine regions. Educating students on sustainable urban planning and community development (SDG 11) can inspire future leaders to create environmentally friendly cities. Furthermore, introducing climate change education (SDG 13) raises awareness about climate impacts in vulnerable regions like the Philippines, prone to natural disasters. Through curriculum integration, Filipino students can become advocates for sustainable development, contributing to a more inclusive, equitable, and environmentally conscious society.
Problems and Challenges in Integrating SDGs into Lessons
One of the primary challenges faced in the Philippine education system is the lack of awareness and understanding of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) among educators and students. Many may not be familiar with the goals, targets, and indicators set by the United Nations.
Another obstacle is the limited access to resources that are aligned with the SDGs. Educators in remote areas or under-resourced schools may struggle to find suitable teaching materials, activities, and assessments that effectively incorporate the goals.
Ensuring that the integration of SDGs aligns with existing curriculum requirements and learning objectives is a significant challenge. Educators need to find ways to incorporate the goals without compromising the core content of their lessons. Additionally, evaluating student understanding and application of the SDGs can be difficult, especially if traditional assessment methods do not capture the holistic nature of sustainability education.
Time constraints within the curriculum pose a significant challenge. Educators may find it hard to develop new lesson plans and activities that effectively incorporate the goals due to packed schedules and standardized testing. Engaging students in discussions and activities can be also challenging, particularly if the SDG topics are perceived as abstract or disconnected from students' daily lives and interests.
Another factor to consider is teacher development. Many educators may lack training opportunities to enhance their understanding of the SDGs and develop the necessary skills to integrate them into their teaching practices effectively. Involving the broader school community in sustainability initiatives aligned with the SDGs may be challenging since it requires the school to engage local government officials and community leaders effectively.
Post a comment